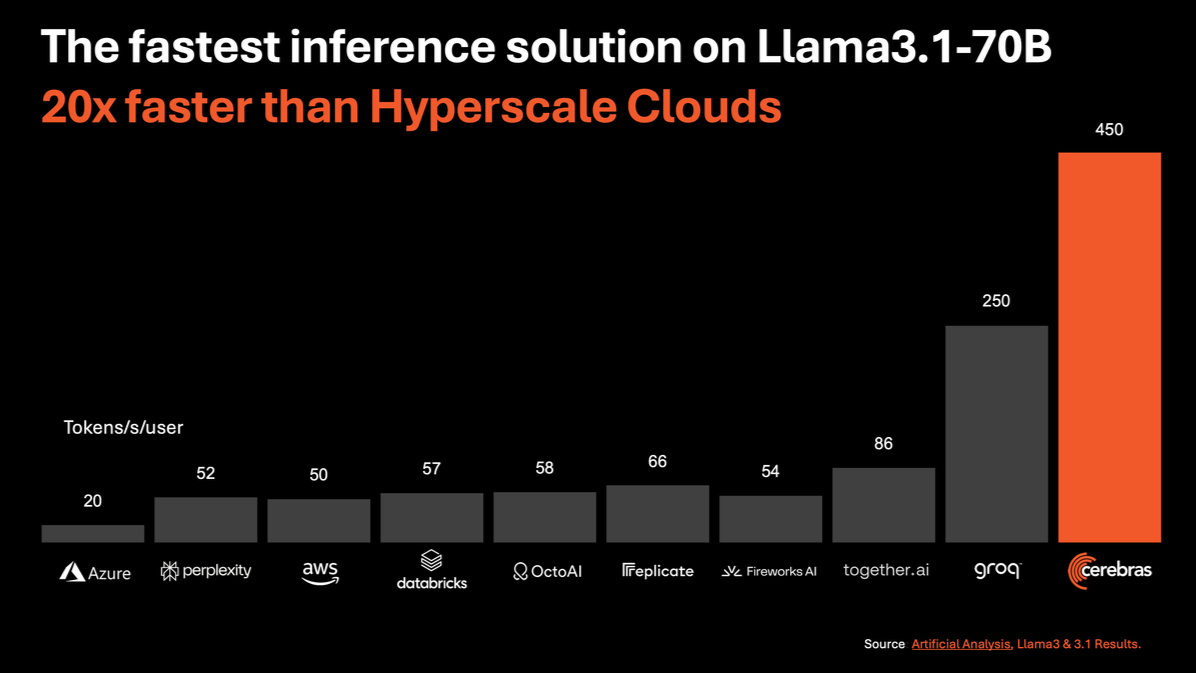
Cerebras Systems, known for its innovative Wafer Scale Engine (WSE), has received a mix of feedback regarding its processors, particularly compared to traditional GPUs like those from Nvidia.
Cerebras is an American artificial intelligence (AI) company that specializes in building computer systems for complex AI deep learning applications. Cerebras Systems launched on Tuesday a tool for AI developers that allows them to access the startup's outsized chips to run applications, offering what it says is a much cheaper option than industry-standard Nvidia processors.
We couldn't find publicly available reviews or comments from users with hands-on experience with Cerebras' Interconnect AI hardware. You can Try the Tool by yourself here.
Startup Claims
High Cost vs. Performance: Cerebras's processors, particularly the WSE, are significantly more expensive than Nvidia's offerings, costing around ten times more than an H100 GPU. Despite this, Cerebras claims that their chips can deliver superior performance for specific AI workloads, executing tasks up to 20 times faster than Nvidia GPUs while being priced at a fraction of the cost for certain applications.

Specialized Use Cases: The WSE is designed specifically for deep learning, boasting over 1.2 trillion transistors and optimized memory architecture. This makes it particularly effective for large-scale AI models, reducing training times from months to mere minutes in some cases. However, this specialization means it may not be suitable for all types of workloads, leading some users to prefer more versatile GPUs
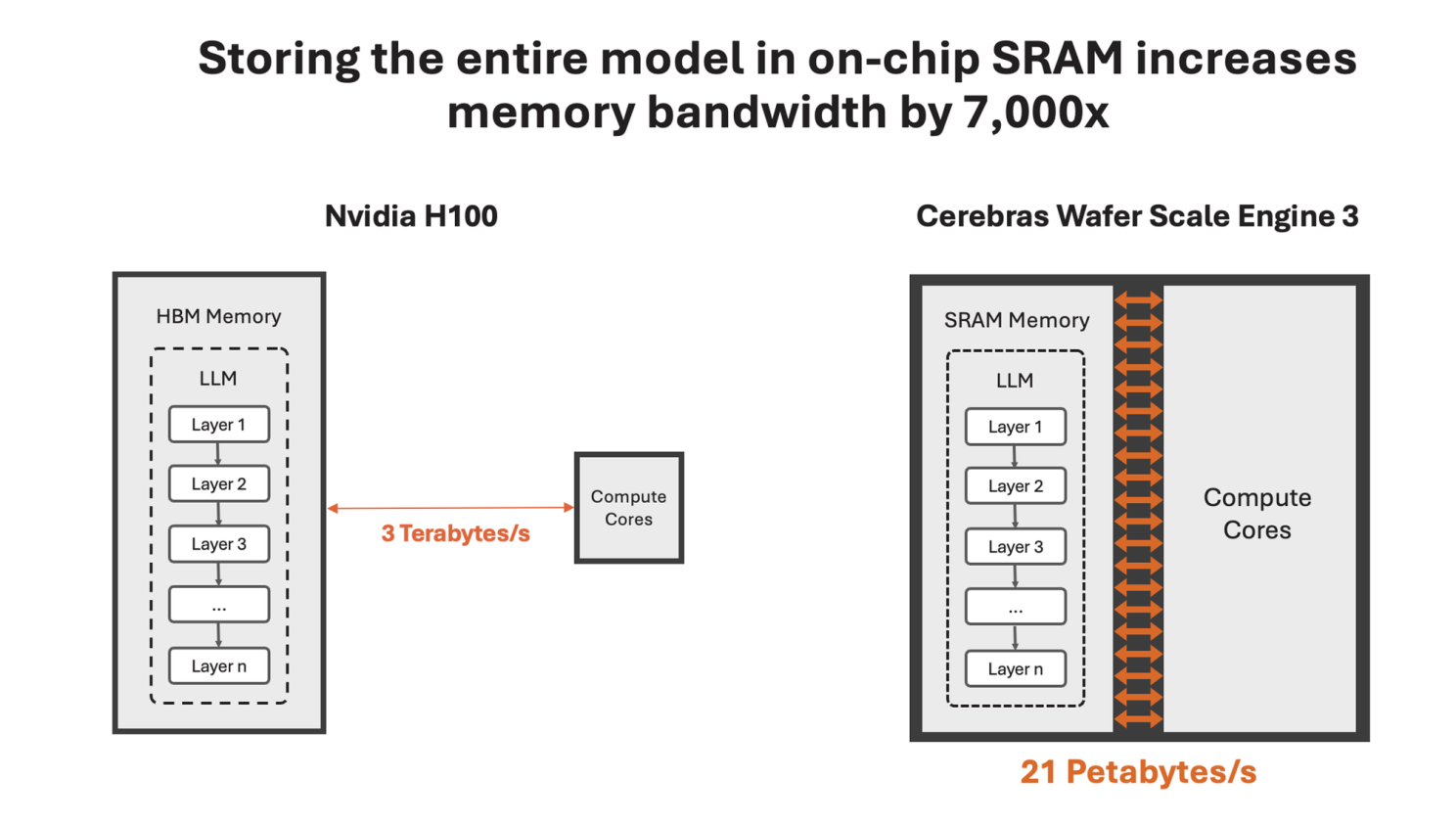
Cooling and Manufacturing Issues: There seem to be significant challenges related to the thermal management of such large chips. The WSE requires advanced cooling solutions due to its high power density, which can complicate its deployment in data centers. There are ongoing discussions about the feasibility of using alternative cooling methods, such as pressurized gases, to enhance performance without overheating.
Inference in the context of AI refers to the process of applying a trained machine learning model to new, unseen data in order to make predictions or decisions.
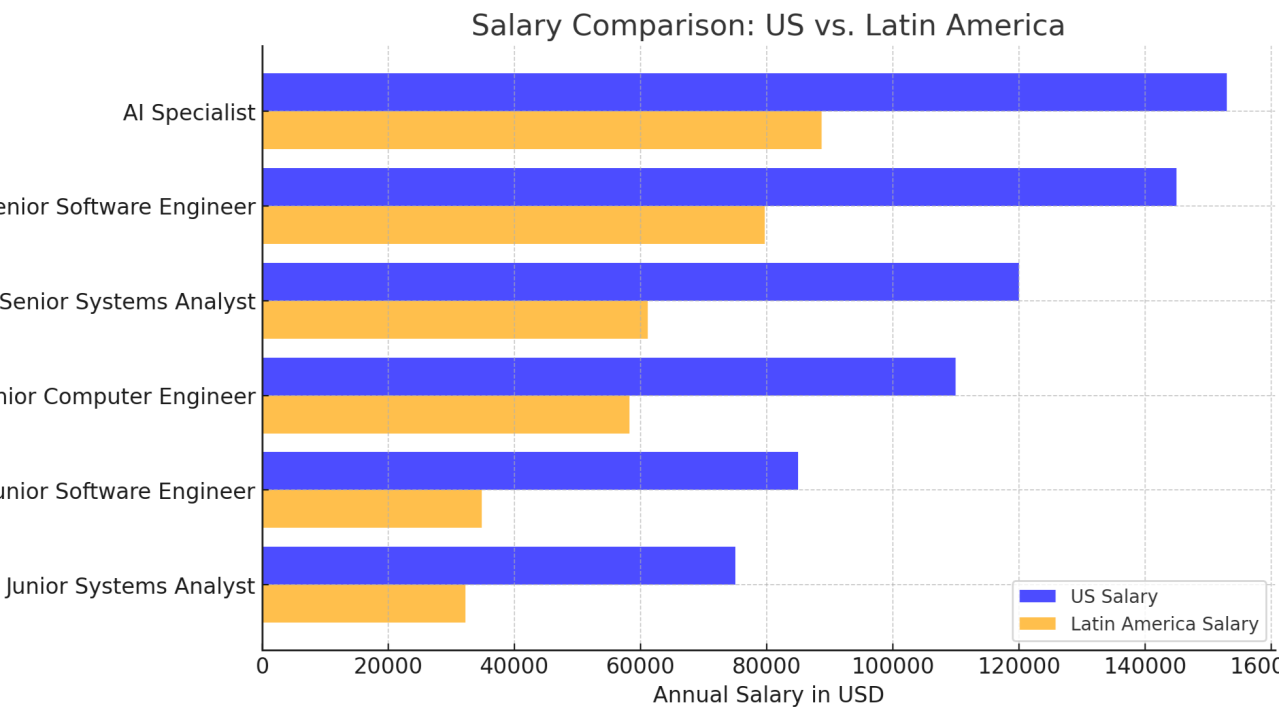
The shortage of technology professionals, including programmers, engineers, and analysts, has intensified in the United States due to the increasing demand for specialized skills and a limited supply of qualified talent.

The need arise from the need to streamline the analysis of exams performed on patients who may present detectable pathologies through imaging studies, assisting the physician in making a faster and more accurate diagnosis.
Researchers at Sakana.AI, a Tokyo-based company, have worked on developing a large language model (LLM) designed specifically for scientific research.

Competing against ChatGPT Enterprise by OpenAI, now Anthropic released its own Claude for Enterprise.

Cerebras Systems, known for its innovative Wafer Scale Engine (WSE), has received a mix of feedback regarding its processors, particularly compared to traditional GPUs like those from Nvidia.

FruitNeRF: Revolutionizing Fruit Counting with Neural Radiance FieldsHow can we accurately count different types of fruits in complex environments using 3D models derived from 2D images without requiring fruit-specific adjustments?